Underground utilities can be difficult to locate. One way to make the process easier is to use a copper-clad steel tracer wire. You can bury this wire alongside the utility line and locate it using a specialized tool.
To detect the tracer wire, you will need a cable locator.
This tool works by sending an electromagnetic signal through the ground. To detect the tracer wire, you need a cable locator that sends an electromagnetic signal through the ground. The tracer wire picks up the signal, which the locator detects.
Before you begin, make sure you have the right equipment.
You will need a cable locator, a ground stake, and a clamp. Before starting, ensure that you have the necessary equipment. You will need a cable locator, a ground stake, and a clamp. Attach the clamp to the ground stake and connect it to the locator.
To begin the detection process, place the ground stake in the ground near the location of the utility line.
Securely attach the clamp to the stake.
Next, turn on the cable locator and select the appropriate frequency.
The frequency should match the frequency of the tracer wire.
Hold the locator close to the ground and move it back and forth over the area where you buried the tracer wire.
The locator will beep or vibrate when it detects the wire.
Once you have located the tracer wire, mark its location on the ground. This will make it easier to locate the utility line in the future.
In conclusion, detecting underground utilities can be challenging, but using a copper-clad steel tracer wire can make the process easier.
With the right equipment and technique, you can quickly locate buried utility lines and avoid costly mistakes.
The Main Range of Copper-Clad Steel Tracer Wire Diameter
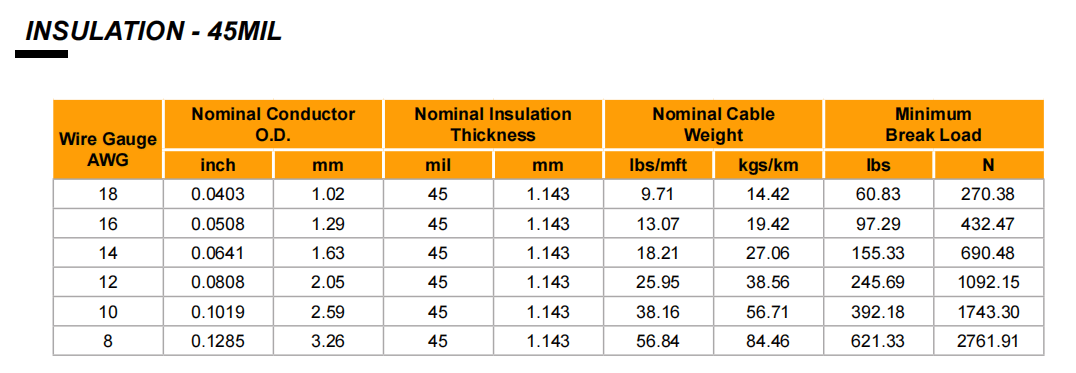
The construction industry commonly uses copper-clad steel tracer wire to locate underground utilities. Manufacturers make this type of wire by coating a steel core with copper. Which provides the strength of steel and the conductivity of copper. One important aspect of copper-clad steel tracer wire is its diameter range.
The diameter of copper-clad steel tracer wire can range from 8to 18 gauge. The gauge refers to the thickness of the wire, with a lower number indicating a thicker wire.
The choice of gauge depends on the size of the utility line being traced. You can use a thinner gauge wire for smaller diameter lines. In areas with high soil resistivity or for larger diameter lines, you typically use thicker gauge wire.
It’s important to note that the diameter of the tracer wire can affect its detectability. Thicker wires may be easier to detect, but they can also be more expensive and difficult to work with. Thinner wires may be more affordable and easier to install, but they may be more difficult to detect.
In addition to the diameter of the wire, other factors can affect its detectability, such as the depth of burial and the type of soil. It’s important to use the appropriate equipment and techniques when locating underground utilities to ensure accurate results.
In conclusion, copper-clad steel tracer wire is an essential tool for locating underground utilities. Its diameter range can vary depending on the size of the utility line being traced and other factors. By using the appropriate size and techniques, you can quickly and accurately locate buried utility lines and avoid costly mistakes.

